Table of Contents
Introduction to Switched Reluctant Motors (SRM)
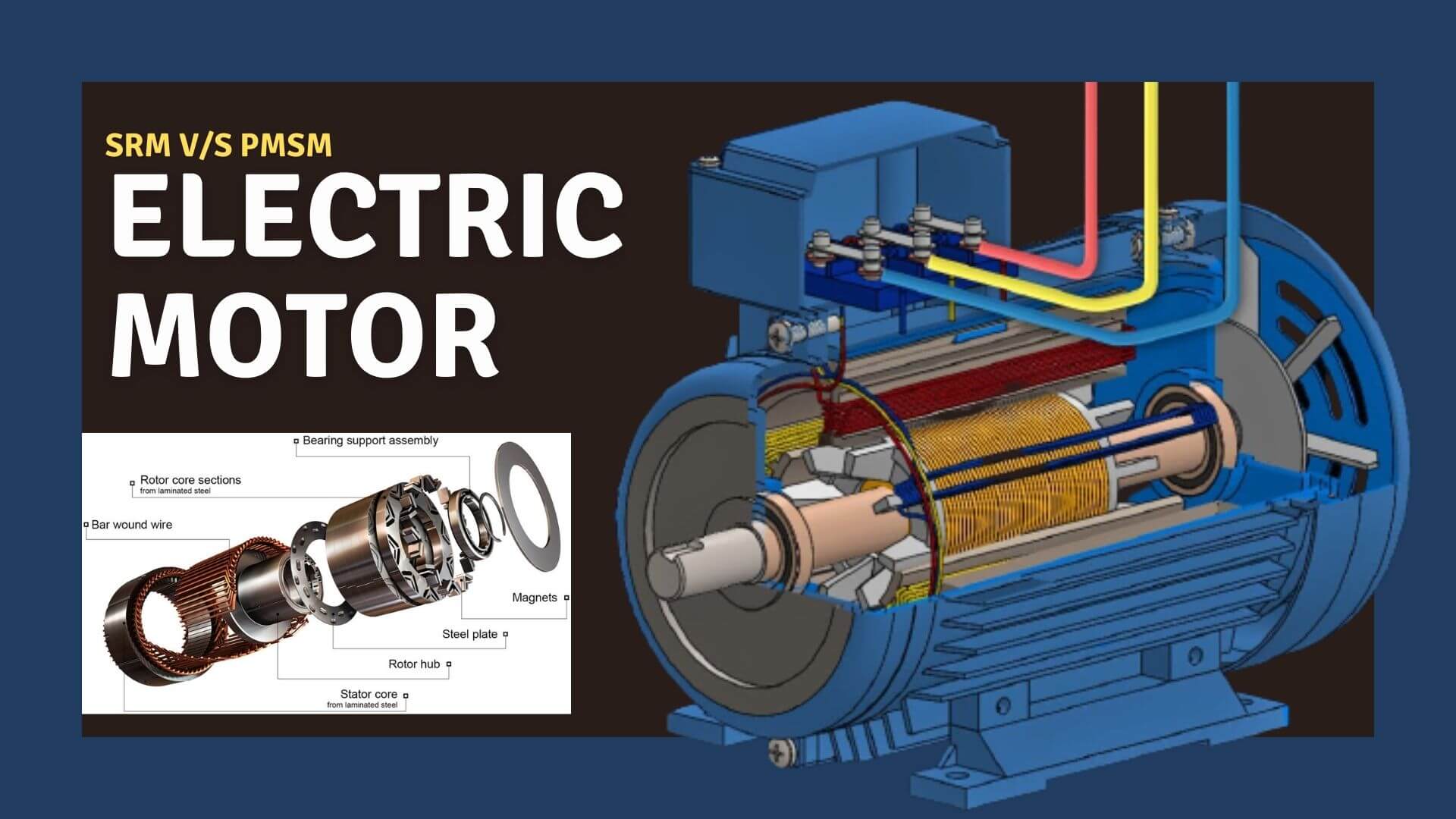
The switched reluctance motor (SRM) is a reluctance torque-driven DC electric motor. Unlike most brushed DC motors, power is routed to stator (case) windings rather than the rotor. It emulates the behavior of an AC motor by switching the DC between the stator windings.
It complicates electrical design because power must be delivered to the various windings via a switching mechanism. Electronic devices can accurately time current switching, making SRM designs easier.
The switched reluctance motor operates on the changing reluctance principle, which implies that the rotor of this motor is constantly aiming to align through the lowest reluctance lane. The rotational magnetic field can be produced with the help of a power electronics switching circuit. 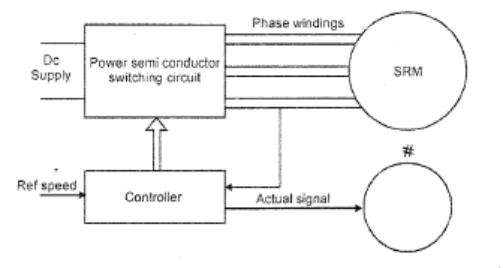
Advantages of Switched Reluctant Motors (SRM)
- Construction is straightforward and robust.
- No windings, slip rings, brushes, etc are included in the rotor as a result it is easier to maintain than other types of motors.
- There’s no static magnet.
- Ventilation is easier as losses take place mostly within the stator.
- Power semiconductor switching circuitry is easier.
- It’s possible to urge very high speed.
Disadvantages of Switched Reluctant Motors (SRM)
- Torque-rippling cause noise pollution at medium to high speeds
- Stator phase winding should be capable of carrying magnetizing current.
- It requires position sensors.
Introduction to Permanent magnet synchronous motors (PMSM)
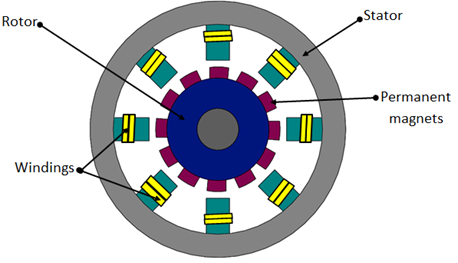
Permanent magnet synchronous motors are a form of AC synchronous motor in which the field is stimulated by permanent magnets, which produce sinusoidal back EMF.
It has the same rotor and stator as an induction motor, but the rotor is a permanent magnet that creates a magnetic field. As a result, the rotor’s field winding does not need to be wound. It is also known as 3-Phase Brushless permanent sine-wave motor. 
When the rotor field poles maintain the revolving magnetic field at synchronous speed and the rotor rotates continuously, the torque is produced. Given this fact, these motors are not self-starting, a variable frequency power supply is required.
Advantages of Permanent magnet synchronous motors (PMSM)
- Torque ripples are absent.
- High-Performance efficiency (output to input ratio)
- Availability in different sizes.
- Smooth torque.
Disadvantages of Permanent magnet synchronous motors (PMSM)
- We need a control system as we can only change the stator current.
- There are no self-starting motors.
- There is a high initial cost involved.
- Performance on PMSM depends on the quality of the magnet used.
Why PMSM or SRM are used rather than traditional and cost-effective Induction Motors to manufacture EVs?
Let’s talk about Induction Motors in brief-
SRM Vs PMSM Motors in Electric Vehicle
The invention was brought up by Nikola Tesla in 1883. The basic principle of the working of induction motors is electromagnetic induction where the magnetic field generated around the conductor induces current due to continuous rotation.
This induction motor functions with the flow of AC induction.
The above-discussed principle of electromagnetic induction creates a minute delay which is known as slip. Due to the induced current flow, there is a noticeable difference between the motor speed due to the magnetic field and the rotating shaft speed.
Therefore, to remember in an easier sense, these induction motors are termed as “Asynchronous Motors”.
Now, as we have an idea about Induction Motors, let us understand why PMSM is better than induction motors.
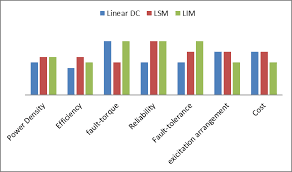
Firstly, PMSM is a synchronous motor whereas the induction motor is an asynchronous motor. Slips produce torque in induction motors, sometimes slips are unnecessary and lead to energy losses and decreasing efficiency of the induction motors.
Secondly, PMSM is designed in such a way that it has a higher performance output compared to Induction Motors. (You can refer to the graph given below when both motors are compared based on power factor).
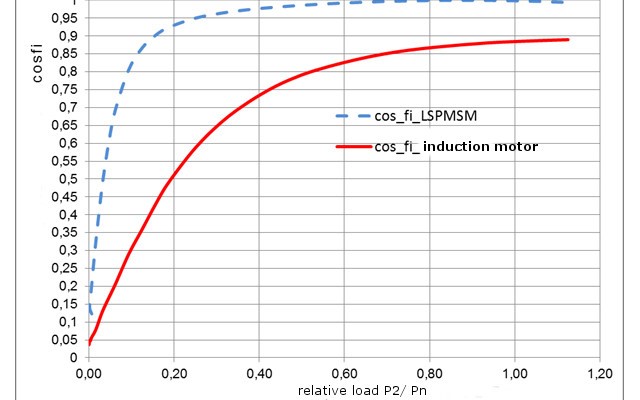
The above graph indicates PMSM’s consistent efficiency under different load ranges. This eventually indicates energy saving during its EV’s running span.
Thirdly, Permanent magnet synchronous motors PMSM can generate torque even at zero speed ensuring smooth pickup and braking operations compared to induction motors.
Lastly, EVs are being manufactured in large masses where the more efficient and sustainable motor will lead the motors’ demand in the EV market.
One of the most controversial and complicated motors amongst different motors. SRM has been understood for a long time yet this wasn’t much in use for electronic advancements.
So why do we use PMSM Motor?
When we compare SRM and IM, they are just better and worse in some situations.
SRM has more power density but lacks in keeping up the power factor against IM. There are more vibrations caused by SRM due to torque ripples while it can generate a huge amount of torque in the shortest time when compared with other electric motors.
It needs to be a better arrangement for operating SRMs (starting and sync). There have been optimization taking place but those are just minor improvements in SRM advancements.
The recent noticeable advancements have been observed in the Tesla Model 3 and Toyota Prius. I am talking about the IPM-SynRM electric motor, Toyota Prius is an HEV with a single magnet piece but it wasn’t revolutionary as the Tesla Model 3.
The EV Markets are rising like never before and everyone is just so excited to notice and learn about the different advancements going on recently.
Top 5 Electric Motor Manufacturers in India
The Rebel EV industry has a large number of electric motor manufacturers: here is the list of the top 5 electric car motor manufacturers in India.
- Tata AutoCorp,
- General Motors,
- Virya Mobility,
- Nidec Corp.,
- Aisin Seiki Co. Ltd., etc.
Advantages of Reluctance Motor
- Simple motor construction.
- Low rotor inertia facilitates high starting torque.
- These motors produce high self-inductance.
- Can produce variable speeds at constant power outputs.
Switched Reluctance motor vs BLDC for EV
- BLDC motors perform better when compared to SRMs at high speeds.
- SRM is more cost-effective than BLDC motors.
- When both these motors are under high power applications, SRM motors perform much better than BLDC motors as SRM are cooler during their operations.
SRM vs IM
- As discussed in this article, SRM has a higher power density than IM.
- Due to high power density, SRM performs operations more efficiently than IM.
- IM is more cost-effective than SRM.






Ꭲhis website was… how do I say it? Relеvant!!
Finally I have found something that helped me.
Many thanks!