India’s Electric Vehicle (EV) market has been developing rapidly, emphasizing reducing air contamination and reliance on foreign oil. In the present scenario, electric mobility is acquiring importance globally. Additionally, India is at a significant stage where the innovation of electric vehicles is being examined and is trying to speed up its adoption. At COP21, the country committed to lessening its carbon impression by 33-55%.0 by 2030. In fact, today, the market is dominated by two-wheeler EVs, with a smaller presence of four-wheeler EVs.
According to MarketandMarkets, with the continuous growth of EV bikes, the Indian electric two-wheeler market is projected to expand at a CAGR of 29.07% and reach $1,028.04 million by 2028. Furthermore, particularly with the rising utilization of commercial vehicles, many industries and service providers endeavor to make electric vehicles inexpensive, simpler to charge, and economical to run. In this context, battery swapping is one solution that has emerged to provide all these benefits for fleet operators.
Battery Swapping: Need for Fleet Operation
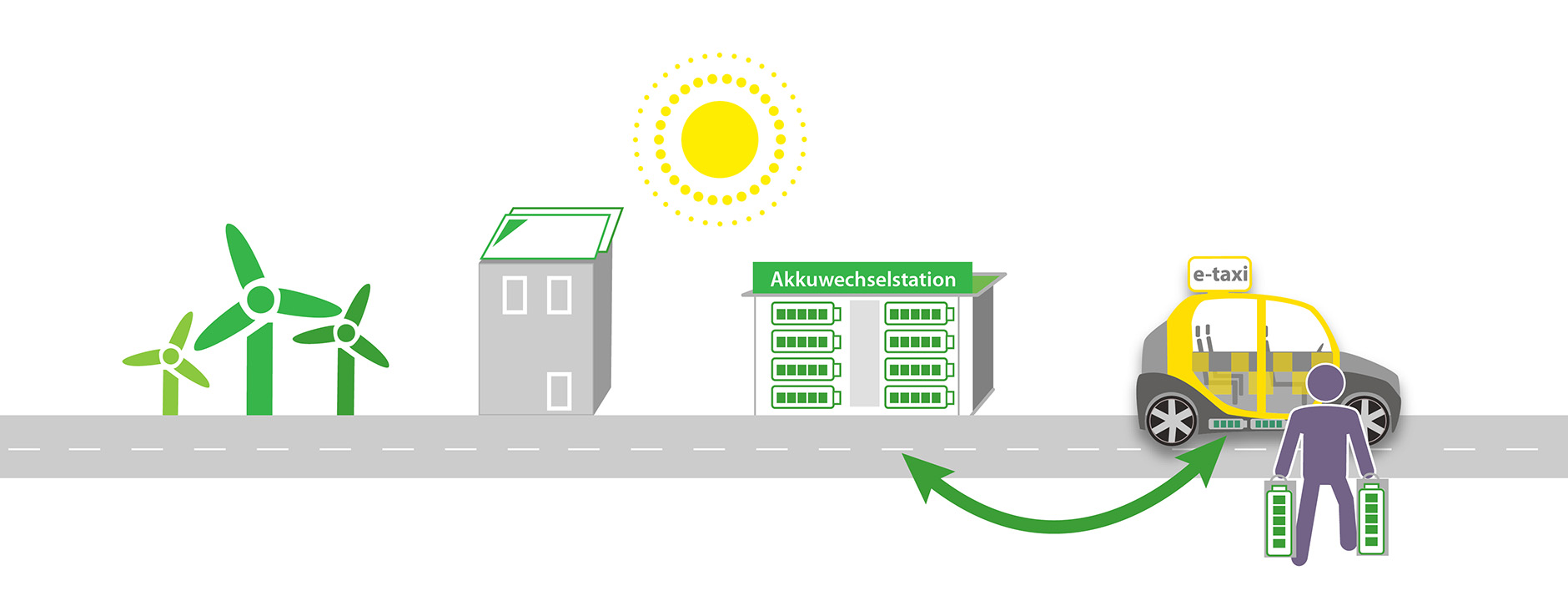
Battery swapping is the technique that exchanges a depleted battery for a fully charged one in order to continue operating a fleet of electric vehicles without interruption. Regarding economics, battery swapping can potentially lower operational costs because electric two-wheelers and three-wheelers are currently more cost-competitive than their ICE equivalents for fleet-based models. As a result, fleet owners can purchase automobiles without batteries, use the battery swapping service to drive them, and lower their initial investments. According to Research and Markets, the Indian electric vehicle battery swapping market is poised to grow at a CAGR of 24.5% to reach $30.96 million by 2027. Adding to it, the economics of battery swapping for fleet operations can vary depending on the specific circumstances, such as the size and type of the fleet, the operational needs and requirements, and the local regulatory environment.
Economics of Battery Swapping
There is no denying the fact that in recent years there have been a few critical developments in the EV landscape of India that were favored by battery swapping. In this context, not only has the corporate industry contributed to boosting the economics of battery swapping, but the government has also made considerate efforts to mainstream EV adoption. In the previous year, the Finance Minister of India declared to carry out a battery swapping policy to inter-operability guidelines to boost the concept. Furthermore, the economics of battery swapping can be examined from both the demand and supply sides:
Demand Side: Battery swapping can offer a cheaper alternative to charging for EV owners, as it eliminates the cost of charging infrastructure and electricity. Furthermore, the technique is convenient as it can reduce downtime for EVs, making it a more attractive option for customers traveling long distances.

Supply Side: The stations for battery swapping require significant upfront investments in infrastructure and batteries. In addition, the maintenance costs and replacing batteries in battery swapping stations can be expensive. The revenue generated from battery swapping stations can come from charging a fee for battery swapping services or from selling refurbished batteries.
In a nutshell, switching from fossil fuel to electric vehicles is inevitable due to the increasing global concerns about environmental sustainability. The inconvenience brought by the battery charging process forestalls the general utilization of electric vehicles. Thus, a battery swapping technique, which the government and industry players emphatically advance, has become promising to boost the future of electric vehicle adoption.
Read More: Pros and Cons of Battery Swapping: An Energy Efficient Solution






Sorry , but where is the economics ?
😂😂😂