Green mobility or Electric vehicle is now becoming a need of the current era, to meet the environmental target of zero-emission. EVs must be sustainable for society and that will be achieved by the Electric vehicle architecture. Vehicle architecture needs to be flexible so it can adopt drivetrain electrification.
ICE vehicle architecture is specific and complex to understand but an advantage point in EV is that there is a new freedom for design, in the design of new components, and implementation in electric car architecture is possible.
Introduction
The electric vehicle drivetrain offers new freedom in terms of electric vehicle architectures while leading to new challenges in terms of meeting all requirements.
Electric vehicles have an electric motor and a battery instead of a combustion engine and a fuel tank. The architecture becomes simple and controllable at the component level. These modifications require extensive adoptions to integrate the battery safely.
When designing the architecture for EV it is mandatory to use modeling and simulation tools, with specific consideration of electric powertrain, including battery, power electronics, electric motors, sensors, and control system.
In ICE engine power production is not uniform because reciprocating components cause mechanical loss hence engine is not self-started to resolve this issue other components are added to the architecture resulting in the engine becoming heavy the other hand Electric vehicle architecture consists of a motor which is self-started and can easily control by the input current.
They produce uniform power and speed at the output because of this reason motor is lighter than ICE.
The Electric vehicle architecture is the backbone of the EVs. Electric vehicle architecture is categorized in the following way
Following are the Types of Electric Vehicle:
- Hybrid electric vehicle
- Plug-in hybrid electric vehicle (PHEV)
- Battery electric vehicle (BEV)
In the above models, there are different potential and different configurations but PHEV has the same drivetrain as of Electric Vehicle.
In Hybrid vehicle architecture, the conventional vehicle is just modified with electric motors, and drive cycle operation is in a way that a fuel-burning engine is most efficient in a small range and at the most efficient operating point it produces less emission.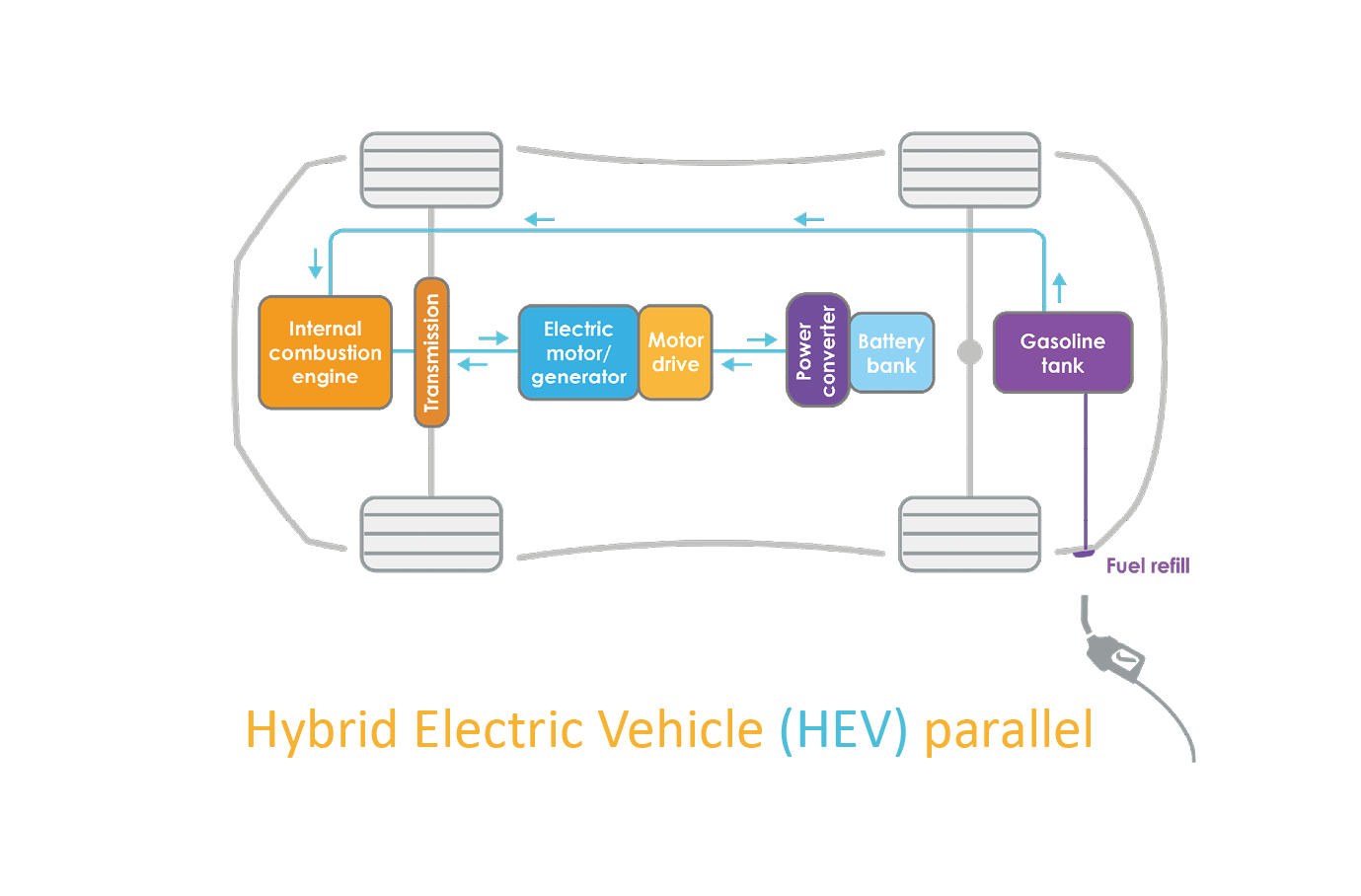
Hybrid vehicle architecture is again classified into 3 different versions:-
- Series hybrid vehicle
- Parallel hybrid vehicle
- Series- a parallel hybrid vehicle
The figure shows the different architecture of the Hybrid vehicles, as per name working is understandable, like if series architecture then energy flow from engine and battery is in series, or if parallel architecture they will operate in the different effective regions in a parallel manner and combination of both architectures is used for best performance of the Electric vehicle.
Plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEV) can be driven with a nearly empty battery because it has a fossil fuel tank, but the plus point is the battery can be charged by during driving on fuel, whereas in Battery electric vehicle(BEV) is run only on battery charge and it has less component in its architecture as shown in the below figures:-
New upcoming modularity in the architecture will smooth the transition of Electric vehicles, different adoptions can be seen in the electric vehicle architecture because of a drastic reduction in the components.
Designing architecture for EVs is a very crucial part of functionality level, the architecture needs to be reliable, efficient, fault-tolerant, and safe.
Electric Vehicle Architecture Powertrains
The Electric vehicle architecture consists of 5 important components and through these components, the powertrain is completed in the EV, such as the Electric motor, Battery pack, Inverter, Charger, DC-DC converter, etc.
Electric Motor
Electric motors provide torque to the vehicle by utilizing electromagnetic fields, and energy supplied by the battery, and the torque is controlled by varying the current flow.
The electric motor gives more than 90% efficiency as compared to ICE, it provides torque with zero speed so it allows the vehicle with a single-gear ratio between motor tires rather than multiple-speed transmission.
Battery Pack
The battery pack is the energy storing device, it must both accept and provide current to the electric machine. Battery packs provide direct current (DC) at their output terminals. Electric machines are controlled by varying an alternating current (AC) waveform.
Invertor
The motor inverter provides this conversion between DC and AC and the torque control functionality.
DC-DC Converter
A DC/DC converter is used to convert power from battery pack voltage down to 12 volts. (E.g. wipers, infotainment system, mirror control)
On-board charger
The charger performs three functions:
- Rectification of AC voltage from the grid to DC voltage.
- Controls the current flowing into the battery pack by controlling the DC output voltage.
- Communicate with the vehicle and off-vehicle equipment.
Battery Management System Components
BMS is used to monitor the state of the battery and is responsible for taking the necessary measurements i.e. SOC, and SOH. Battery Management System (BMS) performs cell balancing to deliver the best efficiency output from a battery pack, and a small ECU is used in this for communication with other components.
Apart from these important components, there are multiple hardware and software used in EV powertrain architecture. There are small monitoring ECUs placed for the specific function and communication is done by CAN protocol.
In Electric vehicle architecture components are selective and the arrangement of such components defines the architecture, plus there is the possibility to arrange more components in the architecture. Following some FAQ on the Electric architecture.
Summary
Different unique Electric Vehicle architectures are coming into the market, and many more are being proposed and researched. In the next 1-2 years there will be various designs with a smooth transition in the architecture and the epic solution will be considered for producing a sensible EV architecture.
EV architecture is a seamless integration of various futuristic technologies, it requires special attention while designing and needs to test and validate in various cases.
FAQs: Electric Car Architecture
EV architecture gives an idea of the complete cycle of the working, arrangement of the components should be placed in a sequence and while designing a vehicle, balance in performance and cost must be achieved therefore the selected architecture plays an important role.
As the name suggests BEV has a motor-driven architecture with suitable selective components but ICE vehicle has a fuel-burning architecture with a complex structure.
Yes, EV architecture has freedom for designing, because of the simple architecture powertrain is smooth, and selective components properly follow the drive cycle because the latest new features can be added to the architecture such as telematics, cloud computing data for the battery status, and running data of the vehicle, updating software in Tesla cars can be done by satellite, and many more features are adding value to it.
Absolutely yes moreover I would say we will have the best new facility for normal EVs which is only available in luxurious conventional cars.
No, the chassis development process follows the same procedure as that of a conventional car.
No, the requirements would be a very low center of gravity, superb handling characteristics, and top speed. So, the range, interior space, and ergonomics could be less important, and the selected architecture would most likely include big battery packs, four in-wheel motors, and high-performance suspension, with a two-seat configuration.




